A technician’s guide to all things related to fire extinguisher inspections, testing, and maintenance (ITM). What needs to be done, who can perform it, and how often it should be conducted.
Fire extinguishers are a staple when it comes to fire protection. They are one of the most common and reliable forms of equipment for building safety and fire prevention. However, simply having fire extinguishers is not enough – they must be regularly inspected, tested, and maintained to certify that they are ready for use in an emergency.
In this article we will discuss everything from the related safety standards to monthly inspections, hydrostatic testing, and more so you can ensure that your organization’s fire extinguishers are compliant and prepared.
Importance of Fire Extinguisher Maintenance
Just like any other equipment, portable fire extinguishers require routine upkeep to remain operational. A lack of upkeep can result in extinguishers that malfunction, are damaged, or become entirely unusable. This can lead to further problems such as legal battles, large fines, severe damages, preventable injuries, and more in the event of a hazardous situation. Ultimately, it is in the best interest of your company, employees, and any other building occupants to maintain your safety equipment.
Not sure what maintenance looks like? Here’s a brief overview:
Maintenance efforts include regular visual inspections, internal examinations, periodic testing, and occasional servicing. These tasks have varying frequencies and steps, which can make them difficult to keep up with, particularly for organizations or buildings with a high volume of extinguishers. By understanding and adhering to industry standards, which we will review in the next section, you can ensure that your fire extinguishers are in peak condition and ready for use.

- Importance of Fire Extinguisher Maintenance
- Standards to Know for Fire Extinguisher ITM
- Monthly Visual Inspections
- Maintenance for Fire Extinguishers
- Internal Examinations
- Hydrostatic Testing Of Fire Extinguishers
- The Importance of Documentation
- Boost Your Efforts With Fire Inspection Software
- Conclusion
- Other Helpful Articles
- Want to learn more about InspectNTrack?
- Navigation
- Quick Links


Standards to Know for Fire Extinguisher ITM
When it comes to fire extinguisher inspections, testing, and maintenance (ITM), there are 2 main safety standards you need to be familiar with: NFPA 10 and OSHA 1910.157.
NFPA 10 is a fire safety standard established by the National Fire Protection Association that presents industry guidelines and best practices for portable fire extinguishers.
This fire extinguisher code provides technicians with the necessary information to properly perform inspections, testing, and maintenance (ITM) on fire extinguishers. Additionally, it dives into topics such as the selection, installation, and recharging of portable fire extinguishers.
NFPA 10 is a resource for inspectors, managers, and safety professionals alike, as it can help with performing duties and maintaining a safe environment.
OSHA 1910.157 is a workplace safety standard established by the Occupational Health and Safety Administration that details government-enforced regulations for portable fire extinguishers.
Similar to NFPA 10, this standard is designed to provide employers and their workers with necessary information regarding the “placement, use, maintenance, and testing of portable fire extinguishers.”
Unlike the NFPA, whose standards are followed on a voluntary consensus, OSHA standards mandate compliance and can result in fines for violations.
Becoming familiar with these two fire extinguisher standards is one of the best ways to prepare for any inspection, testing, or maintenance activities.
Monthly Visual Inspections
What is it?: Monthly visual inspections are quick and basic evaluations of fire extinguishers to make sure they are fully charged, free of damage, and ready for use.
Generally, it is advised to check for a number of things including:
- Extinguishers are in their designated locations and properly mounted.
- There are no obstructions to visibility/access.
- The container has adequate pressure (between 185 – 195 PSI).
- The fire extinguisher is full – confirmed by weighing or lifting.
- Exterior is free of any damage – corrosion, leakage, clogged nozzle.
- There are no missing or broken safety seals.
- Operating instructions are intact and legible.
If any issues are found during visual inspections, they should be documented, reported, and immediately addressed.
Who can perform it?: An initial inspection should be performed during installation by whoever is installing the extinguisher. Following that, pretty much any trained employee can perform a visual inspection.
How often should it occur?: As per NFPA 10(10), Sec. 7.2., visual inspections should be performed during installation and at least once every 30 days (basically monthly) after that.

Maintenance for Fire Extinguishers
What is it?: Fire extinguisher maintenance is a broad term used to describe both routine fixes on extinguishers (such as recharging, replacements, and cleaning the shell) as well as a deeper inspection of all the exintuisher’s mechanical parts (testing seals, operating mechanisms, and reviewing pressure levels) that is performed each year.
Who can perform it?: If trained, generally any worker can assist with routine maintenance. However, a certified fire extinguisher inspector is required to perform the in-depth annual maintenance.
How often should it occur?: NFPA 10(10), Sec. 7.3 outlines that at least once a year, a detailed check of fire extinguishers (annual maintenance) should be performed.
Internal Examinations
What is it?: Internal examinations are a check-up that is performed on stored pressure fire extinguishers (most common type) that require a 12-year hydrostatic test (ex. Dry chemical extinguishers). These examinations are done to ensure that there isn’t any internal damage, that the extinguisher can discharge effectively, and that all components function properly.
Who can perform it?: Internal examinations must be performed by a trained technician and follow the guidance outlined in the manufacturer’s service manual, as per NFPA 10(10), Sec. 7.3.1.2.
How often should it occur?: Generally, internal examinations are performed every 6 years. Some extinguishers do require more frequent examinations, although 6 years is the most frequent time frame. For information about the various frequencies see NFPA 10 (10) Sec. 7.3.1.1.2.
Hydrostatic Testing Of Fire Extinguishers
What is it?: Hydrostatic testing is an NFPA 10 requirement (Sec. 8) that involves testing the extinguisher to verify its strength against rupture. The purpose of this test is to ensure the structural integrity of the fire extinguisher and certify that it can withstand the pressure related to its use.
Who can perform it?: Only individuals with specialized training, equipment, and skills should perform this test. Generally, this is a job that is hired out to a professional.
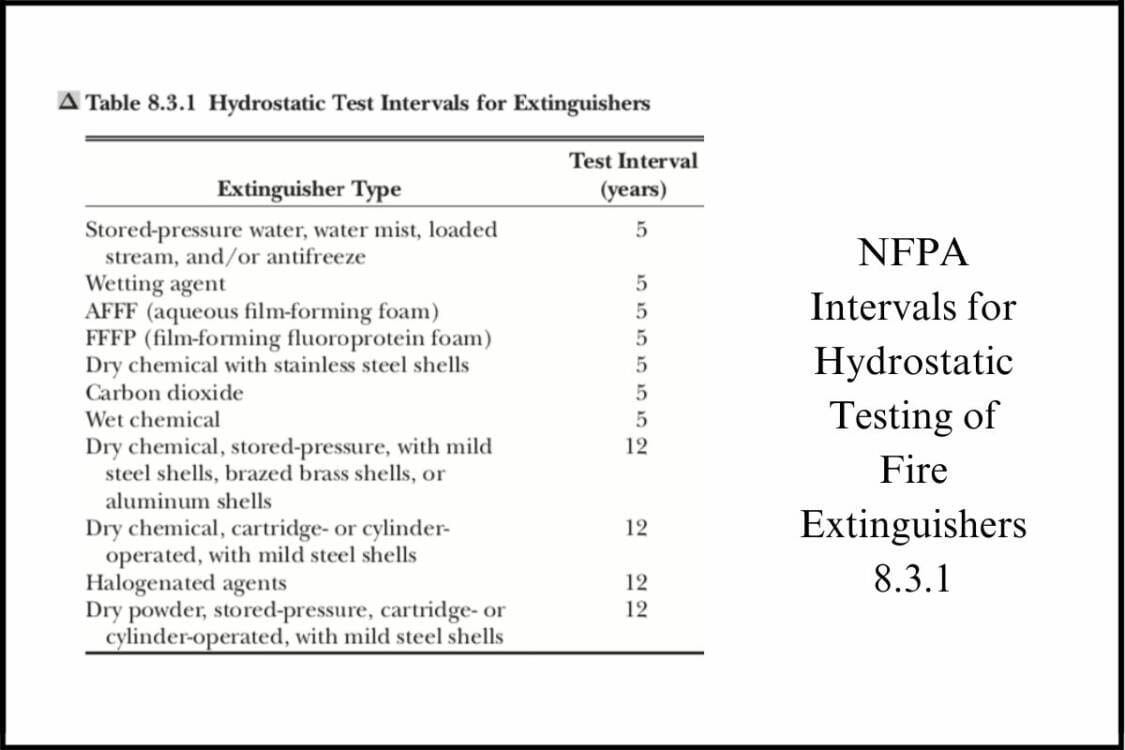
How often should it occur?: The frequency at which hydrostatic testing should occur depends on the type of extinguisher that is being examined. Details for the hydrostatic testing intervals can be found in NFPA 10(10) Sec. 8.3.1.
Intervals for the most common fire extinguishers:
- Pressurized water, water mist, carbon dioxide and wet chemical (e.g. K-type) extinguishers – every 5 years
- Dry chemical extinguishers with stainless steel shells – every 5 years
- Dry chemical extinguishers – every 12 years
The Importance of Documentation
When conducting any fire extinguisher inspections, testing, or maintenance, it is imperative that you document your efforts. Documentation is a necessary element for proving compliance and therefore helping you avoid any violations and fines. Not to mention, organized and complete records help you operate well, maximize safety, and best maintain your equipment.
Here’s what you need to know for documentation:
| Type | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Document All Efforts | Have a central location, either a filing unit, folders, or digital platform to compile all records into. The more thorough and organized you are at documentation, the easier it will be to prove compliance during audits. |
| Monthly Visual Inspections | These need to be recorded either on the fire extinguisher tag/label or paper/digital files and must include the name of the person who conducted the visual along with the month and year. |
| Maintenance Procedures | Annual maintenance checks should be recorded on the extinguisher label/tag and indicate who performed the work, the agency they work for, and when it was performed (month and year). It is best practice to also record this info in your main records. |
| Internal Examinations | Fire extinguishers that receive an internal examination get a verification-of-service collar put around the neck of the container. This collar should state the agency that performed it and date of examination (month and year). |
| Hydrostatic Testing | Low pressure cylinders require a label indicating the person who conducted the test, the date of the test, and the pressure the test was performed at. High pressure cylinders require a stamp with the tester’s identification number and the test date. The stamp may be placed on the shoulder, head, top, neck or foot ring. |
Boost Your Efforts With Fire Inspection Software
Manually tracking fire extinguisher ITM can be overwhelming, especially when you have a lot of extinguishers, various extinguisher types, or multiple facilities to manage. Fire extinguisher inspection software can be a real game changer for helping track your equipment, schedule maintenance, maintain compliance, and document your efforts. Because of these benefits, we want to share a little bit about our software solution and how it can aid you in taking care of your portable fire extinguishers.
There are a wide range of options for software on the market, however, InspectNTrack software has been specifically designed for fire extinguishers and other fire-related equipment. This makes it an ideal resource. Here are some of the primary ways that InspectNTrack can aid your compliance and maintenance efforts:
- Streamlining Inspections with Software: InspectNTrack software simplifies inspections and maintenance by providing a step-by-step walkthrough of inspections for fire extinguishers. These checklists ensure that every element of the system is inspected and tested per regulatory guidelines, which makes the process quick, seamless, and standardized.
- Automating Maintenance/Inspection Schedules: Inspection software can automate maintenance schedules by setting reminders for monthly visual inspections, annual maintenance, and replacements. With this automation, facility managers never miss an inspection deadline, ensuring ongoing compliance with OSHA and NFPA standards.
- Digital Records for Compliance: Inspection software provides a central database to store records of inspections, maintenance, and repairs. This makes it easy to generate reports and retrieve data during audits. If issues arise, the software can log them and help ensure that corrective actions are completed in a timely manner.
- Real-Time Updates and Notifications: Inspection software provides real-time updates on the status of fire extinguishers. Notifications about equipment locations, failures, or needed repairs are sent instantly to the responsible parties, ensuring quick action. With this real-time visibility, facility managers can stay on top of any issues that could impact safety or compliance. Teams can use the software to better collaborate and get the job done.
InspectNTrack is revolutionizing the way we approach fire safety. To learn more about our software and product features, talk to a specialist here.
Conclusion
Routine fire extinguisher inspections, testing, and maintenance are a critical part of ensuring fire safety. By learning about and following safety standards such as NFPA 10 and OSHA 1910.157, you can set yourself up for success. These regulations will help you understand what the ITM requirements are, who can perform them, and how often they should be conducted. Additionally, these resources provide guidelines for proper documentation of efforts. One of the best ways to go about fire extinguisher inspection, testing, and maintenance is to integrate software into your program. Software comes with a range of benefits that can help you manage your tasks and make compliance a high priority. While it may seem intimidating to get started with fire extinguisher ITM, use the resources available and you’ll be just fine!
**Note: While this article provides many helpful details for the inspection, testing, and maintenance of fire extinguishers, it is not a complete report of all the details and requirements found in NFPA 10/OSHA 1910.157. It is merely an overview of the basics for getting started.

